What is blockchain technology? What makes information technology so of import?
Imagine a earth where you can transport money straight to someone without a bank – in seconds instead of days, and you don’t pay exorbitant bank fees.
Or one where y’all store coin in an online wallet not tied to a bank, meaning you lot are your own banking company and take complete control over your coin. You don’t demand a bank’southward permission to access or move it, and never accept to worry about a third party taking it abroad, or a government’s economic policy manipulating it.
This is not a world of the futurity; it is a world that an avid but growing number of early adopters live in right now. And these are but a few of the important blockchain technology use cases that are transforming the way we trust and commutation value. We’ll become into the residual afterward on.
Yet, for many, blockchain technology is still a mysterious or fifty-fifty intimidating topic. Some even remain skeptical that we’ll use this engineering in the future. This skepticism that exists today is understandable considering nosotros’re yet very early in the development and widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
2021 is to blockchain what the tardily 1990s were to the internet. And like the internet, blockchain engineering science is anything simply a fad, it’south here to stay, and if yous’re reading this, you lot’re early on too.
This mail service demystifies blockchain technology. This is your ‘intro to blockchain technology 101’. A complete, easy-to-understand, step by step beginners blockchain breakdown. Y’all’ll acquire everything from what blockchain is and why it matters, to how blockchain works (step by footstep) and what today – tomorrow’s – well-nigh promising blockchain applications may be.
Y’all’ll also walk away from this mail service confident, and well on your manner to making informed, independent blockchain technology investment decisions. And yous’ll exist no slouch if you want to hold your own in conversations with family unit and friends too!
So permit’southward swoop in
Blockchain 101: Blockchain For Beginners
Blockchain engineering science is the concept or protocol backside the running of the blockchain. Blockchain engineering science makes cryptocurrencies (digital currencies secured by cryptography) similar Bitcoin work only like the internet makes email possible.
The blockchain is an immutable (unchangeable, meaning a transaction or file recorded cannot be changed) distributed digital ledger (digital record of transactions or information stored in multiple places on a computer network) with many use cases beyond cryptocurrencies.
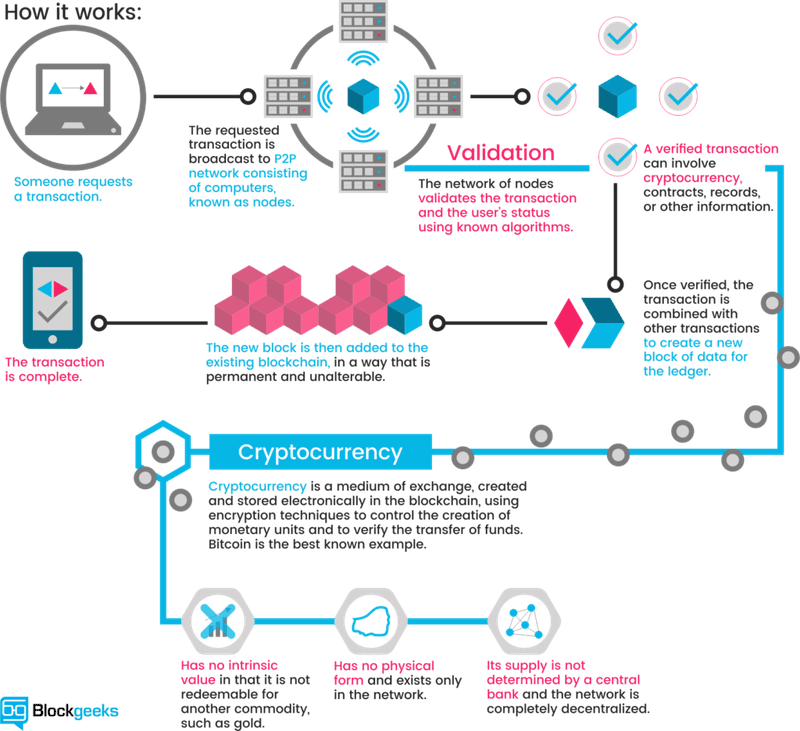
Immutable and distributed are ii key blockchain properties. The immutability of the ledger ways you can always trust it to exist accurate. Being distributed protects the blockchain from network attacks.
Each transaction or tape on the ledger is stored in a “block.” For instance, blocks on the Bitcoin blockchain consist of an average of more than 500 Bitcoin transactions.
The information contained in a cake is dependent on and linked to the data in a previous block and, over fourth dimension, forms a chain of transactions. Hence the word blockchain.
Types of Blockchains
There are four types of blockchains:
1. Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open, decentralized networks of computers attainable to anyone wanting to request or validate a transaction (check for accuracy). Those (miners) who validate transactions receive rewards.
Public blockchains employ proof-of-work or proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms (discussed later). Two common examples of public blockchains include the Bitcoin and Ethereum (ETH) blockchains.
two. Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are non open, they have access restrictions. People who want to bring together crave permission from the organization administrator. They are typically governed past one entity, meaning they’re centralized. For case, Hyperledger is a private, permissioned blockchain.
3. Hybrid Blockchains or Consortiums
Consortiums are a combination of public and private blockchains and contain centralized and decentralized features. For example, Free energy Web Foundation, Dragonchain, and R3.
Take annotation:
There isn’t a 100 pct consensus on whether these are different terms. Some make a stardom between the 2, while others consider them the same thing.
4. Sidechains
A sidechain is a blockchain running parallel to the main chain. It allows users to move digital assets between two different blockchains and improves scalability and efficiency. An example of a sidechain is the Liquid Network.
History of Blockchain
Blockchain isn’t just a database, it’south a new technology stack with ‘digital trust’ that is revolutionizing the way we exchange value and data across the internet, past taking out the ‘gatekeepers’ from the procedure. For a complete and more than detailed deep dive bank check out our article: A Concise History of Blockchain Engineering science
Blockchain history goes back farther than you might imagine, but we’ve condensed it by answering four critical questions:
Who Invented Blockchain?
The start blockchain-like protocol was proposed by cryptographer David Chaum in 1982. Afterward in 1991, Stuart Haber and West. Scott Stornetta wrote most their piece of work on Consortiums.
Only information technology was Satoshi Nakamoto (presumed pseudonym for a person or group of people) who invented and implemented the first blockchain network later on deploying the globe’southward first digital currency, Bitcoin.
Cryptography is a deep and fascinating bailiwick with a history that goes back farther than blockchain. For a richer understanding of how cryptography helps blockchain technology, check out: Why Cryptography Makes Blockchain Unstoppable
Who Owns Blockchain Engineering science?
Because blockchain technology is the technology behind the blockchain, it cannot be owned. Information technology’s similar the net. But anyone can use the technology to run and own their own blockchains.
Who Founded Bitcoin?
Satoshi Nakamoto.
Who Sent and Received the Showtime Bitcoin Transaction?
Nakamoto sent ten bitcoins to Hal Finney, who built the first reusable proof-of-work system in 2004.
How Does a Public Blockchain Work (Pace-past-Footstep)
For a more than in-depth account of the next section, cheque out the thorough discussion in: What is Blockchain Technology and How Does it Piece of work?
Let’s start with an oversimplification.
As a club, we created ledgers to store data—and they have a variety of applications. For example, nosotros use ledgers in real estate to store a firm’s records, such as when alterations were made or the business firm was sold. We also use ledgers in bookkeeping to tape all the transactions a company makes.
Bookkeeping more often than not relies on double-entry accounting to store transactions. Although this is a step-upwards from unmarried-entry accounting that lacks transparency and accountability, double-entry accounting also has its pitfalls: Entries are accounted for separately, making information technology difficult for one counterparty to verify the other’s records.
Records stored using traditional ledgers are too easy to tamper with, meaning you tin hands edit, remove, or add a record. As a result, y’all’re less likely to trust that the information is authentic.
Public blockchains solve both these problems – and the way we trust – by evolving the traditional bookkeeping model to triple-entry bookkeeping: transactions on a blockchain are cryptographically sealed by a third entry. This creates a tamper-proof record of transactions stored in blocks and verified past a distributed consensus mechanism.
These consensus mechanisms too ensure new blocks get added to whatsoever blockchain. An instance of a consensus mechanism is proof-of-piece of work (PoW), often referred to as “mining.”
Mining isn’t universal to all blockchains; it’s but one type of consensus machinery currently used by Bitcoin and Ethereum, though Ethereum plans to motility to another—proof-of-stake (PoS)— past 2022.
Here’s how this process works with Bitcoin. When sending Bitcoin, you pay a minor fee (in bitcoin) for a network of computers to confirm your transaction is valid. Your transaction is and then bundled with other transactions pending in a queue to exist added to a new cake.
The computers (nodes) and then piece of work to validate this listing of transactions in the block by solving a complex mathematical problem to come up with a hash, which is a 64-digit hexadecimal number.
Once solved, the block is added to the network—and your fee, combined with all other transaction fees in that cake, is the miner’s reward. It’s that simple.
Each new block added to the network is assigned a unique central (via cryptography). To obtain each new fundamental, the previous cake’south fundamental and information are inputted into a formula.
As new blocks are continually added through the ongoing mining process, they get increasingly secure and harder to tamper with. Anyone caught trying to edit a record will but exist ignored. All future blocks then depend on information from prior blocks—and this dependency from 1 block to the next forms a secure chain: the blockchain.
You can meet this depicted below for house records stored on the blockchain. For instance, Cake 2 provides a key after taking all the data from Block ane into account (including the primal) and inputting it into a formula. Block iii, in turn, provides a new key after taking all the information from Cake i and Block 2 into account (including the primal) and inputting it into a formula. So, the process repeats itself indefinitely.
Now, allow’s dig deeper, exploring proof-of-work (Prisoner of war) vs. proof-of-stake (PoS) and the blockchain trilemma, which are fundamental to the public blockchain’s functioning.
Proof of Work (Pow) vs. Proof of Pale (PoS)
A public blockchain functions through consensus mechanisms: the process for validating transactions without a third party like a bank.
PoW and PoS are two such mechanisms. While their goal—to reach a consensus that a transaction is valid—remains the same, how they get there is a little different.
What Is Pw?
PoW, the
technical term for mining, is the original consensus mechanism. Information technology is still used past Bitcoin and Ethereum every bit of writing only, as mentioned, Ethereum will move to PoS past 2022. PoW is based on cryptography, which uses mathematical equations only computers can solve.
The example in the previous section of how blocks get added to the Bitcoin Blockchain explains this organisation.
The two large problems with PoW are that it uses a lot of electricity and can only process a limited number of transactions simultaneously (seven for Bitcoin). Transactions typically take at to the lowest degree ten minutes to complete, with this delay increasing when the network is congested. Though compared to the days-long wait required to wire money beyond the world, or even to clear a check, Bitcoin’south 10-minute filibuster is quite remarkable.
Other consensus mechanisms were created to solve these Pow problems; the most popular being PoS.
What Is PoS?
PoS still uses cryptographic algorithms for validation, but transactions get validated by a chosen validator based on how many coins they hold, also known equally their pale.
Individuals aren’t technically mining, and in that location’southward no block reward. Instead, blocks are ‘forged.’ Those participating in this process lock a specific number of coins on the network.
The bigger a person’south stake, the more mining power they accept—and the higher the chances they’ll exist selected as the validator for the adjacent block.
To ensure those with the near coins aren’t e’er selected, other option methods are used. These include randomized block selection (forgers with the highest stake and everyman hash value are called) and coin age selection (forgers are selected based on how long they’ve held their coins)
The results are faster transaction times and lower costs. The NEO and Nuance cryptocurrencies, for instance, tin can send and receive transactions in seconds.
Blockchain or Scalability Trilemma: Decentralization, Security, and Scalability
About blockchain projects are built effectually three cadre properties: decentralization, scalability, and security. Developers are constantly trying to residue these aspects, so one isn’t compromised.
But they often take to sacrifice i for the others. The ‘blockchain trilemma,’ concept was first coined the ‘scalability trilemma’ by Ethereum founder, Vitalik Buterin.
Let’s look at these concepts in more than detail and explore the tradeoffs:
Decentralization
Decentralization ways at that place’s no fundamental point of control. Instead, decisions are fabricated via consensus over a distributed network of computers.
There is, however, one significant tradeoff: speed. Sending transactions takes longer because multiple confirmations are required to validate a transaction. Hence why Bitcoin is slow.
Scalability
Scalability is the ability of the system to cope with a growing number of transactions. Scalability is crucial for mass adoption because any organisation needs to operate efficiently equally more people employ it.
Below is a rough breakup of how many transactions Ethereum, Bitcoin, and credit card companies can procedure per second:
- Bitcoin: 7 per second
- Ethereum: 30 per second
- Credit cards: 5,000 credit card transactions per second with the power to procedure much more if needed. Visa, for example, tin process upwardly to 24,000 transactions per 2nd.
Only achieving scalability ofttimes comes at the expense of decentralization. EOS, for example, promises a maximum of 4000 TPS just has come up under criticism for being too centralized.
Security
Security is the ability of a blockchain to be protected from attacks. Unfortunately, exchanges and source lawmaking have been hacked on many occasions, suggesting that many developers focus on scalability and decentralization at the expense of security.
What Is the Departure Betwixt Bitcoin and Ethereum Blockchains?
Bitcoin and Etherum are the two biggest cryptocurrencies and blockchains, so discussing and comparing them makes sense.
Bitcoin Basics
The Bitcoin network is a public, decentralized peer-to-peer payment network that allows users to send and receive bitcoins without a banking concern getting involved. The digital currency or bitcoin token uses the ticker symbol BTC, and is the only cryptocurrency traded on the Bitcoin network.
Transactions are recorded using a digital ledger, and nodes ensure the Pw consensus mechanism is followed (or that mining happens). For many, Bitcoin seems complicated, but information technology isn’t when you view it as a combination of three things:
- A peer-to-peer payment system: You can send money (BTC) from i person or company to another without the need for a bank. Sending money this style is faster, more secure, and cheaper than using traditional methods.
- A decentralized organisation like the net, and so it’s non controlled by one entity and cannot be stopped past a tertiary party.
- A store of value like aureate (often called digital golden), but much easier to transfer than gold.
Ethereum Basics
In 2013, after traveling, coming together with bitcoin developers, and discovering Bitcoin’s limitations, Vitlaik Buterin decided to amend upon the Bitcoin blockchain and built Ethereum.
The Ethereum network is a public, decentralized peer-to-peer network. Like Bitcoin, it uses nodes and allows users to ship and receive cryptocurrency—in this case, Ether.
The network is much more a payment arrangement—it was primarily created to deploy decentralized applications (dapps) and smart contracts.
Dapps are simply ‘decentralized apps,’ or estimator programs that interact with the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts, nevertheless, operate on the Ethereum blockchain, and are contracts that automatically execute without an intermediary once certain atmospheric condition (written into reckoner lawmaking) are met. For example, a smart contract could be programmed to ship a designated person a portion of your Bitcoin when you die.
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin Blockchains
In summary, Bitcoin and Ethereum networks are public, decentralized peer-to-peer networks with their ain tokens: bitcoins and Ether. Both rely on cryptography, and both use digital ledger applied science.
For a complete Ethereum vs. Bitcoin match up check out our deep dive post: Ethereum Vs Bitcoin: What’s the Departure?
But they differ significantly in purpose and capability. Bitcoin is a decentralized payment system and a shop of value. Its blockchain is a database of all bitcoin transactions and tracks their ownership. Ethereum is more than a payment organization and allows smart contracts and apps to be built on it, making it a more than sophisticated blockchain.
What Are the Benefits of Blockchains Over Traditional Finance?
- Trustless: The blockchain is immutable and automates trusted transactions between counterparties who practice not need to know each other. Transactions are only executed when programmed atmospheric condition are met by both parties.
- Unstoppable: Once the weather condition programmed into a blockchain protocol are met, an initiated transaction cannot be undone, inverse, or stopped. Information technology’south going to execute and nix – no bank, government, or third party – tin stop it.
- Immutable: Records on a blockchain cannot be changed or tampered with – Bitcoin has never been hacked. A new block of transactions is only added afterwards a complex mathematical problem is solved and verified by a consensus mechanism. Each new block has a unique cryptographic key resulting from the previous block’s information and key existence added into a formula.
- Decentralized: No single entity maintains the network. Unlike centralized banks, decisions on the blockchain are made via consensus. Decentralization is essential considering it ensures people can easily admission and build on the platform, and in that location are multiple points of failure.
- Lower Price: In the traditional finance organisation, you pay third parties like banks to process transactions. The blockchain eliminates these intermediaries and reduces fees, with some systems returning fees to miners and stakers.
-
Peer-to-Peer:
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, let you ship money direct to anyone, anywhere in the world, without an intermediary like a depository financial institution charging transaction or treatment fees. - Transparent: Public blockchains are open-source software, so anyone can admission them to view transactions and their source code. They can even use the lawmaking to build new applications and suggest improvements to the code. Suggestions are accustomed or rejected via consensus.
- Universal Banking: 2 Billion people globally practice not have a banking company account. Because anyone can access the blockchain to store money, it’s a bully way to depository financial institution the unbanked and protect against theft that can happen due to belongings cash in physical locations.
What Are the Disadvantages of Blockchains?
Public open up source blockchains are not without their hazards and challenges. Here is a list of the top concerns:
ane. Environmental Impact
Blockchain networks like Bitcoin use a lot of electricity to validate transactions, leading to ecology concerns. For example, Bitcoin consumes more than electricity than a pocket-sized, medium-sized European state, and Bitcoin mining is threatening China’s climate change goals.
However, many would contend that Bitcoin is held to higher ecology standards than anyone and anything. This may be true, especially if you consider that the blockchain and Bitcoin are an alternative to the traditional finance system that uses much more electricity and has a much larger environmental impact.
A study by Galaxy Digital suggests Bitcoin free energy consumption is less than half that of the traditional banking system. If anything, you could contend that Bitcoin is a step in the right management for the surround.
No i is saying that making strides to lowering the carbon footprint shouldn’t be on the agenda (this is already happening with some mining farms shifting to renewable energy sources similar solar panels and the El Salvadoran President calling for a program to utilize geothermal energy (volcanoes) to mine Bitcoin).
Merely it’south crucial to maintain a balanced view when viewing the price, ecology touch on, and blockchain benefits.
2. Personal Responsibility
One of blockchains and cryptocurrencies’ nearly significant advantages is also its biggest weakness. When you invest in public open-source blockchains by mining or buying cryptocurrencies and shop it in your cryptocurrency wallet (your wallet is like your depository financial institution account, except only you can access it and have the passwords), only you control your money.
Yous are your own depository financial institution— and this is great! But if you lose your seed phrases – the list of words that give you access to recover your wallets – there is no recourse (compared to banks where you can reset your password). Your money is lost forever.
Unsurprisingly, a big portion of Bitcoin remains permanently lost. Co-ordinate to some estimates, 20% or 3.7 1000000 of the currently minted Bitcoin is probably lost forever.
3. Growing Pains
Even though public blockchains remain more efficient than traditional banking systems, decentralization comes at the cost of scalability. Trying to grow blockchain networks to global capacity, in turn, is the root cause of speed inefficiencies. It’s why, as we saw, Bitcoin and Ethereum tin can only process a maximum of seven and 30 transactions, respectively, compared to Visa’s 24,000.
Luckily solutions are being built to better scalability and the speed of transactions. For example, the lightning network allows transactions to happen off the Bitcoin blockchain to speed up transactions. On Ethereum, many innovative Layer ii (L2) solutions are being developed to amend scalability and speed including rollups, zero-knowledge proofs and side bondage.
4. Imitation Narratives
Some cryptocurrencies are undoubtedly used in unlawful activity. The most famous example is Silk Road: people laundered money and bought drugs on the platform using Bitcoin.
However, this is no unlike from the illegal activity that constantly happens when people utilize other currencies like the Dollar.
This false narrative that cryptocurrencies are but or mainly used for illicit activities only delays their inevitable adoption, which tin hugely do good anybody, including the financial system.
Promising Blockchain Utilize Cases and Killer Applications
For an fifty-fifty more in-depth discussion of the most interesting and disruptive blockchain use cases as of 2021 check our guide: Disruptive Blockchain Engineering science Use Cases 2021
Blockchain engineering science is currently used across various industries similar supply chain, healthcare, retail, media and advertising, financial services, insurance, travel and transportation, oil and gas, and gaming.
Here are some promising use cases:
- Cryptocurrencies: The ‘killer app’ of blockchains today is internet coin. Cryptocurrencies permit you transfer value faster and cheaper beyond borders without a bank. Besides Bitcoin and Ethereum, other digital currency examples include Polkadot (DOT), NEO, Cardano (ADA), Tether (USDT), Binance Coin (BNB), and Litecoin (LTC).
- Smart Contracts: These blockchain applications are contracts that automatically execute without an intermediary one time conditions written into the computer code are met.
- Decentralized Banking: The utilize of blockchain applied science is also proliferating in banking. For example, many banks similar Barclays, Canadian Imperial Bank, and UBS are interested in how blockchain can brand their back-office settlement systems more efficient.
- Video Games/Art: You may have heard Crypto Kitties—a game launched on the Ethereum blockchain. Ane of the virtual pets in the game was sold for over $100,000.
- Peer-to-peer Free energy Trading: People buy or sell energy straight without an intermediary.
- Supply chain and logistics tracking: Blockchain is being used to rails precious metals’ origins and foods. For example, Walmart and IBM worked together to create a food traceability arrangement based on open up-source ledger technology, making it easier to trace contaminated food.
- Healthcare process optimization: Blockchain can speed up the time required to pay health insurance payments to patients and store and deeply share medical data and records.
- Real estate processing platform: Property ownership records can exist deeply stored and verified on the blockchain. These records cannot be tampered with, and then you tin trust they’re authentic and more than easily verify property ownership.
- NFT marketplaces: These are marketplaces that let you lot to buy nonfungible tokens (NFTs): digital tokens of things like paintings and habiliment.
- Music royalties tracking: Blockchain tin can trace music streams and immediately pay those who contributed to a vocal.
- Anti-money laundering tracking system: Authorities can more easily track the original source of money because every transaction on the blockchain is recorded and leaves backside a tamper-proof trail.
- Personal identity security: Traditional systems for storing identities are insecure and fragmented. Blockchain provides a unified, immutable, and interoperable infrastructure so yous can shop and manage records securely and efficiently.
- New insurance distribution methods: For example, peer-to-peer insurance, parametric insurance, and microinsurance.
- Automated Advertizing Campaigns: Advertisers tin can use smart contracts to automate advertising campaigns, e.g., an audience is simply shown an ad when specific criteria are met.
How to Invest in Blockchain Engineering
With blockchain offering some promising apply cases, helping many companies get more efficient, and attracting big companies like Amazon and Tesla, information technology can be an attractive investment.
But at that place are risks: It’south a new technology, and many projects will not pan out. And so, invest simply what you can beget to lose, practise your own research to decide if the project (or initial coin offering) is worth investing in, and decide what level of exposure you want.
For instance, you tin can go more than exposure by investing in cryptocurrencies directly instead of an exchange-traded fund (ETF).
That being said, here are a variety of ways you tin can invest in the blockchain depending on your goals and gamble tolerance:
-
Buy shares in companies using blockchain
(e.g., Visa, Walmart, and Siemens) on traditional stock exchanges like the NYSE. Yous can buy shares past using an online banker such as Vanguard and Edification (U.S.). - Invest in companies with Bitcoin on their balance sheet, e.one thousand., Square, WeWork, MicroStrategy, and Tesla. Once more, employ an online broker to buy shares.
-
Buy cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin
or Ethereum directly on Centralized Finance (CeFi) or Decentralized (DeFi) exchanges. Centralized exchanges were the norm in the crypto earth until decentralized exchanges arrived. With centralized exchanges, you don’t have your own private keys, and the substitution is the custodian for storing your funds. Decentralized exchanges are peer-to-peer, and there’s no intermediary. Examples of CeFi exchanges include Binance, Kraken, Bittrex, Bitfinex, Luno, and Coinbase. Examples of DeFi exchanges include Uniswap, Compound, KyberSwap, Airswap, IDEX, SushiSwap, Balancer, and Totle. - Invest in crypto exchange-traded funds (ETFs). ETFs are a basket of securities that runway an asset or alphabetize you tin purchase or sell on an substitution throughout the solar day. For example, many traditional ETFs will include bonds, currencies, commodities, and stocks and rail the S&P 500 Alphabetize. In the crypto infinite, yous get a variety of ETFs you tin invest in, such as a Bitcoin ETF that tracks the price of Bitcoin. Each ETF will differ depending on who problems it. Companies that offer ETFs include Grayscale, Galaxy Digital, and Gemini.
- Invest in crypto mining companies such every bit Riot, Hive, and Marathon. Many mining companies let investors participate indirectly by offering equity in their companies. To invest in Anarchism, apply an American-based online broker like Robinhood. To invest in Hive and Marathon, use a Canadian-based broker like Questrade, TD Direct Investing, or BMO InvestorLine.
- Buy crypto hardware and mine cryptocurrency yourself. While Bitcoin mining requires a large capital outlay, at that place are other tokens y’all tin can mine for a reasonably low barrier to entry. For case, Helium miners cost roughly $500 and mint HNT using the ‘proof of coverage’ consensus protocol to verify new blocks. Get started with cryptocurrency mining by reading our short guide on Bitcoin mining.
- Invest in mining pools. An culling to mining cryptocurrency yourself is to join a mining pool. Mining pools puddle together the computational ability of others on the network to improve the chances of mining a block. The rewards for all blocks mined are shared amongst miners in the pool. Slush Pool is a popular mining pool.
Blockchain Companies to Invest in 2021
If you’re looking to become started with crypto investing, we’ve created a comprehensive step-past-step guide y’all can follow to get started here: How To Invest in Cryptocurrencies: The Ultimate Beginners Guide
Here is a comprehensive list of public blockchain companies to invest in. We have segmented them based on these categories: banking, supply concatenation, wellness care, energy, insurance, travel, existent estate, exchanges, and mining.
These public companies are either using blockchain, have cryptocurrency on their balance sheets, allow you to trade cryptocurrency, or are mining cryptocurrency.
*Technically, Binance is not a public company, merely yous can invest in it past purchasing their ain digital currency (BNB). You lot can use their currency to pay for transaction and trading fees on the commutation. This is too truthful for DeFi exchanges like Uniswap, 1inch, and PancakeSwap.
Traditional Finance and Blockchain Investment Strategies
In some ways, the procedure of investing in shares and cryptocurrencies is the aforementioned. Kickoff, y’all can purchase cryptocurrencies on exchanges like you lot can buy shares through an online broker.
Second, y’all are likewise able to apply traditional investment principles to investing in cryptocurrencies and the blockchain. For example, you tin invest the same corporeality of money into Bitcoin each calendar month regardless of toll (dollar-cost averaging) to remove whatever emotion out of the investment process.
But there are as well investment strategies that are unique to the blockchain and cryptocurrencies, like yield farming.
Read on to learn well-nigh ten mutual traditional finance and blockchain investment strategies you can use when investing in public blockchain companies and cryptocurrencies.
Overview of 10 Major Investment Strategies
-
-
Growth Investing:
Investors await for companies that demonstrate above-boilerplate growth. Investors using this strategy will oft still invest in shares even if they seem expensive.To narrow downward your search, focus on industries currently doing well or have historically performed. With the blockchain technology marketplace expected to grow in size, there are bound to exist several companies with strong growth potential. -
Value Investing:
Investors look for undervalued companies, east.g., their cost doesn’t fully reflect their value. Successful value investing often requires that you hold your shares for the long term. -
Dividend Growth Investing:
Investors invest in companies that have a history of paying out dividends. You tin can look at a company’s financial statements to meet if they pay out dividends. Expect for a yield of between 2-6%. -
Indexing:
This is more than of a cautious and passive investment strategy, but indexed investors ofttimes outperform more active investors. These investors typically invest in an index fund.An index fund consists of pooled funds from investors, is managed by a fund manager, and automatically invests in the companies of a specific index like the South&P 500 to effectively runway confronting the alphabetize’s performance.Information technology is different from an ETF in that you can simply buy or sell index funds at the stop of the day and non throughout. An example of a cryptocurrency index fund is the Bitwise 10 Crypto Index Fund (BITW). -
Twenty-four hour period Trading:
Day trading is a more active and ambitious brusque-term trading strategy. Investors oft trade throughout the day to capitalize on small-scale market movements to make a profit. Day traders volition use technical analysis to develop trade ideas effectually how the market volition movement. Day trading cryptocurrency is equally lucrative and risky due to highly volatile assets. -
Algorithmic Trading:
Also known every bit automatic trading, this investment strategy involves using reckoner programs to execute trades based on pre-programmed instructions such every bit price, time, etc. A large portion of the American market consists of algorithmic trading. AlgoTrader is an automated trading plan you can use for Bitcoin trading. -
Contrarian Investing:
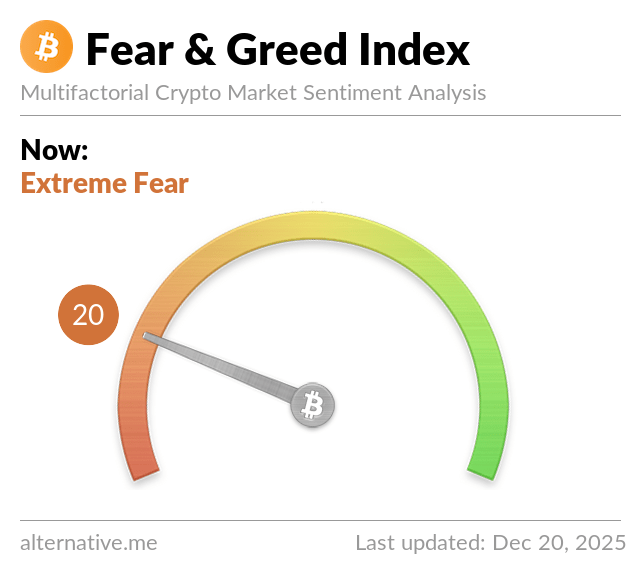
Contrarian investors purposely become against the marketplace sentiment. They buy when people are selling and sell when people are buying.By following the Bitcoin Fear and Greed Index, you tin can get a skilful idea of the prevailing sentiment in the Bitcoin marketplace and then do the opposite: buy when people are fearful and sell when they’re greedy (encounter Fear & Greed Index below). -
Arbitrage:
This strategy involves taking advantage of price differences of the same asset between markets. You purchase the asset in one marketplace and then sell it for a higher toll in another.Because cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin often differ in price between countries, there are great opportunities to profit from this strategy.In a nutshell, traders will buy cryptocurrency on an overseas exchange (for a lower toll) and then transfer it to a local exchange and sell it for a college price.Equally Business concern Tech reports, you can make 2-four% per trade using the right investment platform. Just brand sure you lot follow local exchange control laws considering in that location are unremarkably limits to how much local currency you can move beyond the borders. -
Yield Farming:
This blockchain-specific investment strategy involves lending your cryptocurrency to someone else via smart contracts.The lendee pays you a fee for your services. Yield farmers often motility their cryptocurrency between unlike lending platforms to maximize returns. A few yield farming platforms include Compound Finance, Aave, and MarketDAO. Learn more almost DeFi yield farming. - Diversification: Spread your risk and invest in different assets and companies to limit your overall downside while exposing y’all to more opportunities to make money. Diversification is more than just an investment strategy; it’due south a smart mode to invest that well-nigh fiscal experts and brokers encourage.This strategy works well for traditional finance and cryptocurrency.In traditional markets, y’all can spread adventure across bonds, coin markets, and shares— and even diversify your share portfolio by investing across industries.For cryptocurrencies and blockchain, y’all tin can invest in different public blockchain companies and too cryptocurrencies with different employ cases like Bitcoin (payments), Ethereum (smart contracts), Monero (privacy), and XRP (cross border payments).If you really want to prioritize diversification, you should invest beyond traditional and crypto markets, and rebalance your portfolio as needed.
-
Growth Investing:
How can businesses benefit from blockchain?
Let’s look at the business organisation-specific advantages of blockchain technology.
– As mentioned above, the blockchain is a great way to build trust among entities that have never worked together. As such, it is an excellent way for businesses to work together without requiring a trusted third political party.
– The blockchain tin can assist create a consortium of businesses and provide an operational structure with no central “leader.” This tin allows multiple businesses to interact effectively and share information.
– The fact that all information stored within blockchains are immutable has game-irresolute security implications. It’south no longer possible for malicious centralized parties to tamper with crucial data.
– By removing the need for trusted third parties, the overall organizational costs go down significantly. Plus, taking away these intermediaries drastically increases operational speeds. For example, Walmart used blockchain to trace the source of sliced mangoes in seconds. Normally, this process would accept a week.
– The blockchain is a major benefaction for companies that rely on or operate supply bondage. The blockchain’south transparency helps fix a bulk of the issues nowadays in traditional supply chain structures. For example, not but has Walmart successfully applied blockchain in their supply concatenation via IBM, but the medical industry is actively using the tech in their crackdown on counterfeit medication.
Blockchain Is the Present and the Future
With many promising existent-world utilize cases like faster cross-edge payments and smart contracts, blockchain engineering is here to stay.
Every bit more companies realize how the blockchain can assist them, they’ll commit more resources, money, and time into the engineering science—and even more use cases will emerge. While we understand that blockchain engineering science will remain a complex topic for many, information technology actually doesn’t accept to be for you.
We hope this guide gave you the conviction to have conversations with friends and acquaintances almost the blockchain and that information technology demystified and simplified an often scary topic. Refer to it whenever y’all demand to brush upward on any blockchain concepts.
Most importantly, nosotros promise information technology lit a small burn in you to learn fifty-fifty more nigh a technology that’s fundamentally changing the way we trust and substitution value.
Source: https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-blockchain-technology/
 RosyandBo.com Trusted Information and Education News Media
RosyandBo.com Trusted Information and Education News Media



